| |
TM 10-3930-653-14&P
4-7-9. SPARK PLUGS
4-7-9-1. DESCRIPTION
The spark plugs are of the resistor type, having 14
mm (0.55 in) threads and 0.7 to 0.8 mm (0.028 to 0.031
in) gap. Inspection and cleaning should be made in
accordance with the periodic maintenance schedule.
Note
All spark plugs
installed
on
an
engine, must be of the same brand
and heat range.
4-7-9-2. INSPECTION
(1)
Remove spark plug wire by pulling on boot, not on
wire itself.
(2)
Remove spark plugs.
(3)
Check electrodes and inner and outer porcelains of
plugs, noting the type of deposits and the degree of
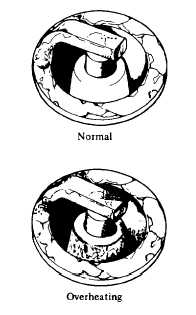
electrode erosion. See Fig. 7-69.
Normal: Brown to grayish-tan deposits and slight
electrode wear indicate correct spark plug heat
range.
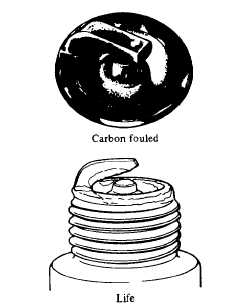
Carbon fouled: Dry fluffy carbon deposits on the insulator
and electrode are mostly caused by slow speed
driving, weak ignition, too rich a fuel mixture, dirty
air cleaner, etc.
It is advisable to replace with plugs having hotter
heat range.
Oil fouled: Wet black deposits show excessive oil
entrance into combustion chamber through worn
rings and pistons or excessive clearance between
valve guides and stems. If the same condition
remains after repair, use a hotter plug.
Overheating: White or light gray insulator with black or
gray brown spots and bluish burnt electrodes
indicate
engine
overheating.
Moreover,
the
appearance results from incorrect ignition timing,
loose spark plugs, low fuel pump pressure, wrong
selection of fuel, a hotter range plug, etc. It is
advisable to replace with plugs having colder heat
range.
Fig. 4-149. Spark Plug
4-83
|