 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 10-3930-631-34
from the positive side of the battery through the 400
provide additional inputs to the contactor logic to open if
amp power fuse, the closed forward contactor contacts
an improper condition is detected.
to the drive motor. When the drive motor operates, the
(4) The power switch and drive regulator
truck moves in the direction selected.
modules regulate operation of the drive motor through
(4) The forward and reverse contactors are
the armature and free wheeling diodes.
equipped with interlocks to prevent current flow to both
(5) The plugging circuit and plugging relay
sides of the drive motor simultaneously. The interlocks
reduce the control cycles to prevent damage to the
are mechanically operated whenever the applicable
control and motor when direction of travel is reversed.
contactor opens or closes.
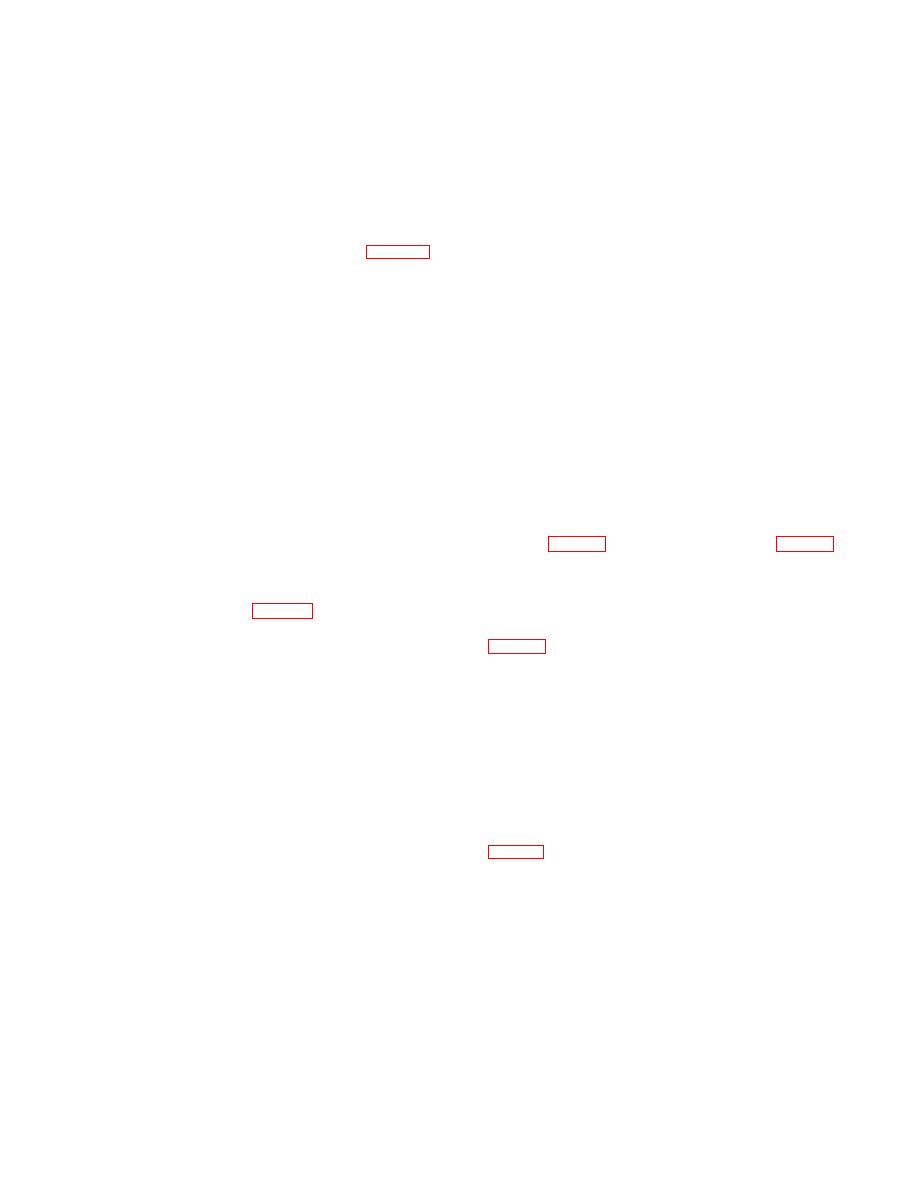
(6) The
temperature
coefficient
resistor
(5) The hydraulic pump contactor (fig. 2-7)
monitors the temperature of the control heat sink. When
operates in much the same manner. With the key
temperature rises excessively the resistor will reduce
switch, seat switch and emergency cutout switches
the on time of the power switch module .
closed, movement of the control valve levers will close a
(7) Additional safeguards are supplied by four
pump switch. Current then flows from the positive side
thermal relays. If the operating temperature of the drive
of the battery through the 400 amp power fuse, 15 amp
motor rises above a safe operating point, the thermal
control fuse, to the contactor panel and the pump con-
relay will open and halt motor operation. After allowing
tactor coil to the negative side of the battery. A set of
the relay to cool the points will close and operation can
normally open contacts on the pump contactor close
be resumed.
and send current to the pump motor. Current flows
(8) Another thermal relay protects the hydraulic
through the pump motor back to the negative side of the
pump motor in the same manner. Two thermal relays
battery.
monitor the temperature of the hydraulic oil in the
(6) The contactor panel also contains the diode
reservoir and will shut down the hydraulic pump circuit if
suppressor module. The suppressor module contains
the temperature becomes too high.
hash filters to suppress voltage spikes
when the
9-3. Operation
hydraulic pump coil, horn button, contactor coils and
a. General. The following is a more detailed
hourmeter are de-energized.
description of the control operation. By using the wiring
(7) All fuses are mounted in the contactor
diagram (fig. 9-1) and the block diagram (fig. 9-2) the
panel. The four 15 amp control fuses are mounted in
operation can be followed in detail. The points below are
the upper left corner of the contactor panel.
general and will aid in understanding the operation.
e. Static Panel
(1) Any connections, junctions or terminals with
(1) The static panel (fig. 9-6) is mounted in a
the same identification are electrically common.
compartment on the left side of the frame. For easy
(2) All contacts and components are illustrated
access the panel is mounted on a hinged door. When
the door is opened and swung down into place, the
otherwise specified.
static panel components are accessible for maintenance
(3) Location of components on the schematic
procedures.
diagram will have no bearing on their physical location
(2) Mounted on the static panel are the control
within the fork lift truck.
circuit module, three power switch modules, three drive
b. General Operation.
regulator modules, the plugging relay and three large
(1) The basic time-ratio control is a fixed-
capacitors. The armature diode and free wheeling diode
frequency type. The frequency is non-adjustable and is
are mounted in the front portion of the static panel. A
approximately 300 Hz. The on time of the control, which
positive temperature coefficient resistor is mounted in
is determined by the position of the
speed
the heat sink.
potentiometer, is controlled by the operator's accelerator
(3) The control circuit module sends the current
pedal. The on time is controllable from zero to 100 %
through the power switch and drive regulator modules.
Circuits within the module
9-5
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |